Navigating Challenges in the Metal Injection Molding Industry
The Metal Injection Molding (MIM) industry, renowned for producing intricate metal components with high precision, faces several challenges that impact its growth and efficiency. Addressing these challenges is crucial for manufacturers aiming to maintain competitiveness and meet evolving market demands.
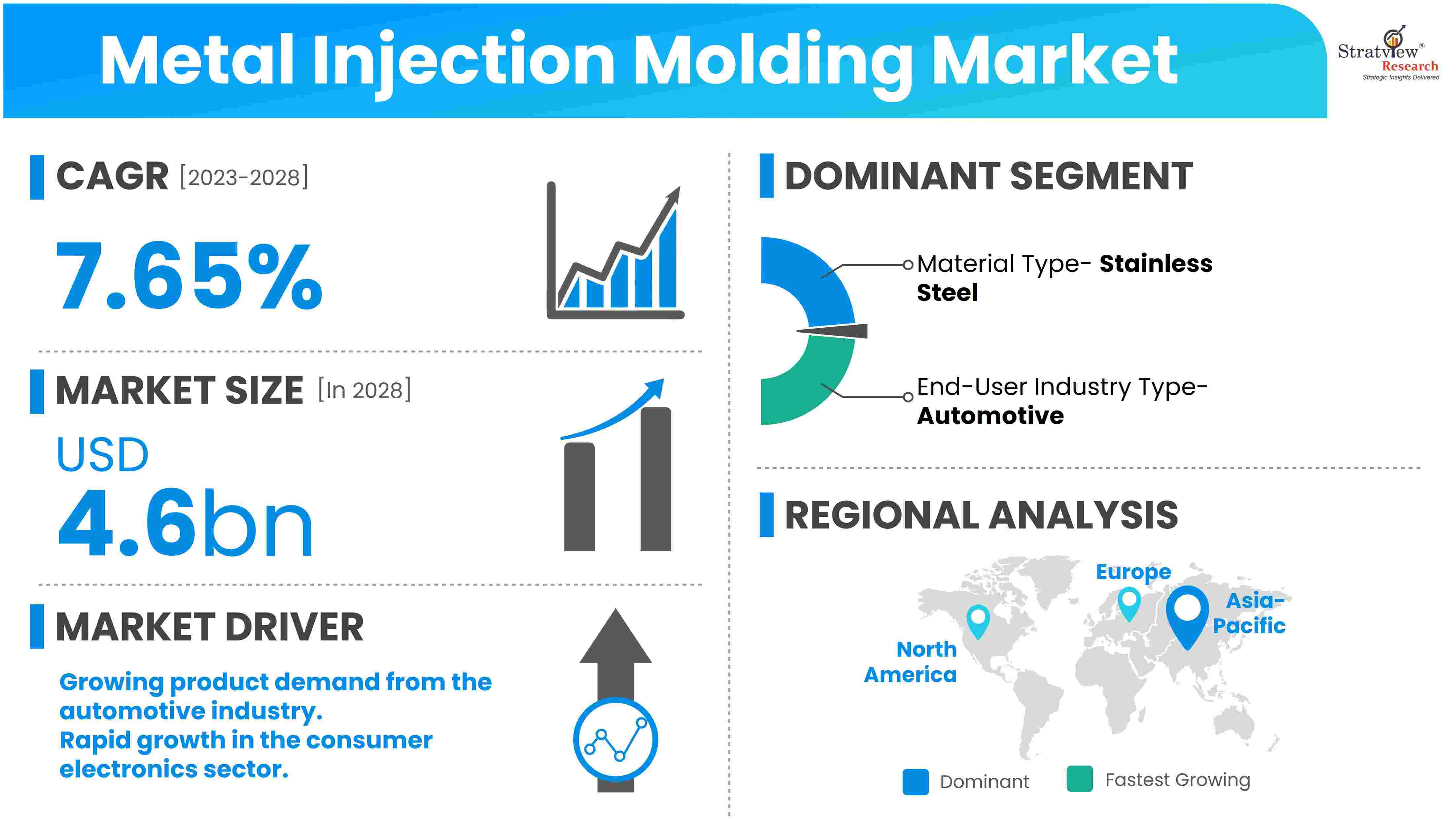
According to Stratview Research, the metal injection molding market was estimated at USD 2.94 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 7.65% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 4.6 billion in 2028.
1. Material Limitations and Quality Control
Ensuring consistent material quality is paramount in MIM. Variations in metal powders or binder compositions can lead to defects such as porosity and shrinkage, compromising the structural integrity of the final products. Implementing stringent quality control measures and collaborating closely with material suppliers are essential to mitigate these issues.
2. High Production Costs
The MIM process involves multiple stages—mixing, molding, debinding, and sintering—each contributing to the overall production cost. While MIM is cost-effective for large-scale production, the initial setup and material costs can be substantial. Manufacturers are exploring automation and process optimization to reduce expenses and enhance efficiency.
3. Design and Customization Constraints
Balancing complex design requirements with manufacturability poses a significant challenge. While MIM allows for the creation of intricate geometries, certain design limitations exist, such as wall thickness constraints and the need for uniform material distribution. Collaborative design approaches and advanced simulation tools can help navigate these constraints effectively.
4. Competition from Alternative Technologies
Emerging manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), offer alternative solutions for producing complex metal parts. These technologies can sometimes provide faster prototyping and greater design flexibility, posing a competitive threat to MIM. To stay ahead, MIM manufacturers are investing in research and development to enhance process capabilities and material options.
5. Skilled Workforce Shortage
The specialized nature of MIM requires a workforce with expertise in metallurgy, material science, and process engineering. However, there is a growing shortage of skilled professionals in these areas. Investing in training programs and fostering partnerships with educational institutions can help bridge this gap and ensure a steady pipeline of qualified personnel.
Conclusion
While the MIM industry faces notable challenges, proactive strategies focusing on quality control, cost reduction, design optimization, technological innovation, and workforce development can effectively address these issues. By embracing these approaches, MIM manufacturers can navigate the complexities of the industry and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Whats New
- Shopping
- Wellness
- Sports
- Theater
- Religion
- Party
- Networking
- Music
- Literature
- Art
- Health
- Oyunlar
- Food
- Drinks
- Fitness
- Gardening
- Dance
- Causes
- Film
- Crafts
- Other/General
- Cricket
- Grooming
- Technology

