Integrating Patient-Centric Approaches into Partial-Onset Seizure Care
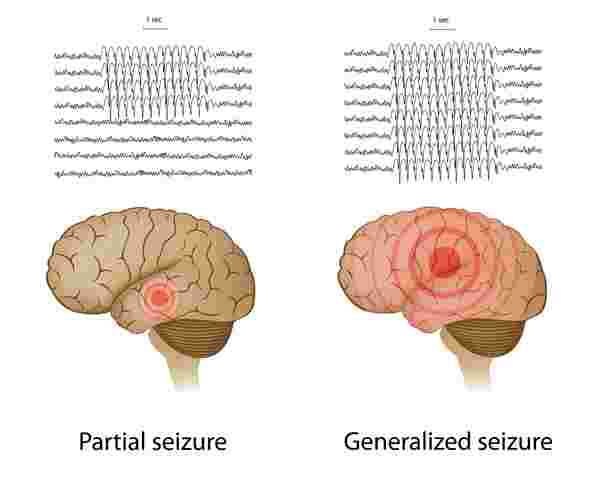
Introduction:
In the realm of epilepsy management, the importance of patient-centric care is gaining recognition. This segment explores the evolving landscape of patient-centered approaches in the context of partial-onset seizures, emphasizing the significance of personalized care, shared decision-making, and the holistic well-being of individuals living with epilepsy.
Pregabalin 75 mg capsules can handle this types of pain with ease.
1. Shared Decision-Making in Treatment Plans:
· Individualized Treatment Goals: Recognizing that each person's experience with partial-onset seizures is unique, healthcare providers are increasingly involving individuals in the formulation of treatment plans. Establishing individualized treatment goals takes into account factors such as seizure frequency, medication tolerability, and lifestyle preferences.
· Risk-Benefit Discussions: Engaging individuals in discussions about the risks and benefits of different treatment options fosters informed decision-making. This shared decision-making process allows individuals to actively participate in choosing interventions that align with their values and priorities.
2. Patient Education and Empowerment:
· Comprehensive Information: Providing individuals with comprehensive information about epilepsy, partial-onset seizures, and available treatment options is integral to empowerment. Accessible educational materials, workshops, and online resources contribute to a better understanding of the condition and its management.
· Self-Management Strategies: Equipping individuals with self-management strategies empowers them to actively participate in their care. This may include strategies for stress reduction, recognizing potential triggers, and adhering to treatment plans. Patient education programs often incorporate these elements to enhance self-efficacy.
3. Psychosocial Support Services:
· Mental Health Support: Recognizing the psychosocial impact of partial-onset seizures, healthcare providers are increasingly integrating mental health support into epilepsy care. Counseling services, support groups, and access to mental health professionals help individuals navigate the emotional challenges associated with epilepsy.
· Peer Support Networks: Peer support networks connect individuals with others who share similar experiences. These networks provide a platform for sharing coping strategies, exchanging insights, and fostering a sense of community. Peer support can be instrumental in reducing feelings of isolation.
4. Cultural Competence in Care Delivery:
· Understanding Cultural Perspectives: Recognizing the influence of cultural factors on individuals' beliefs and practices is essential for delivering culturally competent care. Healthcare providers are increasingly attuned to cultural nuances, ensuring that care plans align with the cultural context of the individual.
· Language Accessibility: Language barriers can pose challenges in healthcare communication. Efforts to enhance language accessibility, through interpreter services or multilingual resources, contribute to effective communication and understanding between healthcare providers and individuals with epilepsy.
5. Incorporating Quality of Life Measures:
· Holistic Assessment: Beyond seizure frequency, healthcare providers are incorporating measures of quality of life into their assessments. Understanding the broader impact of epilepsy on daily functioning, relationships, and overall well-being informs more comprehensive care planning.
· Routine Quality of Life Checks: Integrating routine assessments of quality of life allows healthcare providers to monitor changes over time and tailor interventions accordingly. These assessments provide a dynamic understanding of the individual's evolving needs and challenges.
Conclusion:
As the field of epilepsy care evolves, a paradigm shift towards patient-centric approaches is reshaping the way partial-onset seizures are managed. By embracing shared decision-making, prioritizing patient education and empowerment, providing psychosocial support, addressing cultural considerations, and incorporating quality of life measures, healthcare providers are striving to enhance the overall well-being of individuals living with epilepsy. These patient-centric initiatives contribute to a more personalized and holistic approach to partial-onset seizure care, promoting not just seizure control but also the empowerment and improved quality of life for those affected.
- Whats New
- Shopping
- Wellness
- Sports
- Theater
- Religion
- Party
- Networking
- Music
- Literature
- Art
- Health
- Spiele
- Food
- Drinks
- Fitness
- Gardening
- Dance
- Causes
- Film
- Crafts
- Other/General
- Cricket
- Grooming
- Technology

