According to Stratview Research, the concrete fiber market was estimated at US$ 1.31 billion in 2021 and is expected to exhibit a healthy CAGR of 5.0% over the forecast period, reaching a valuation of US$ 1.8 billion by 2027.
In the dynamic world of construction, where strength and resilience are paramount, the Concrete Fiber Industry stands out as a key player in reinforcing the very foundations of our built environment. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of the Concrete Fiber Industry, shedding light on the diverse types of fibers, applications, and the pivotal role they play in enhancing the structural integrity of concrete.
Understanding Concrete Fibers:
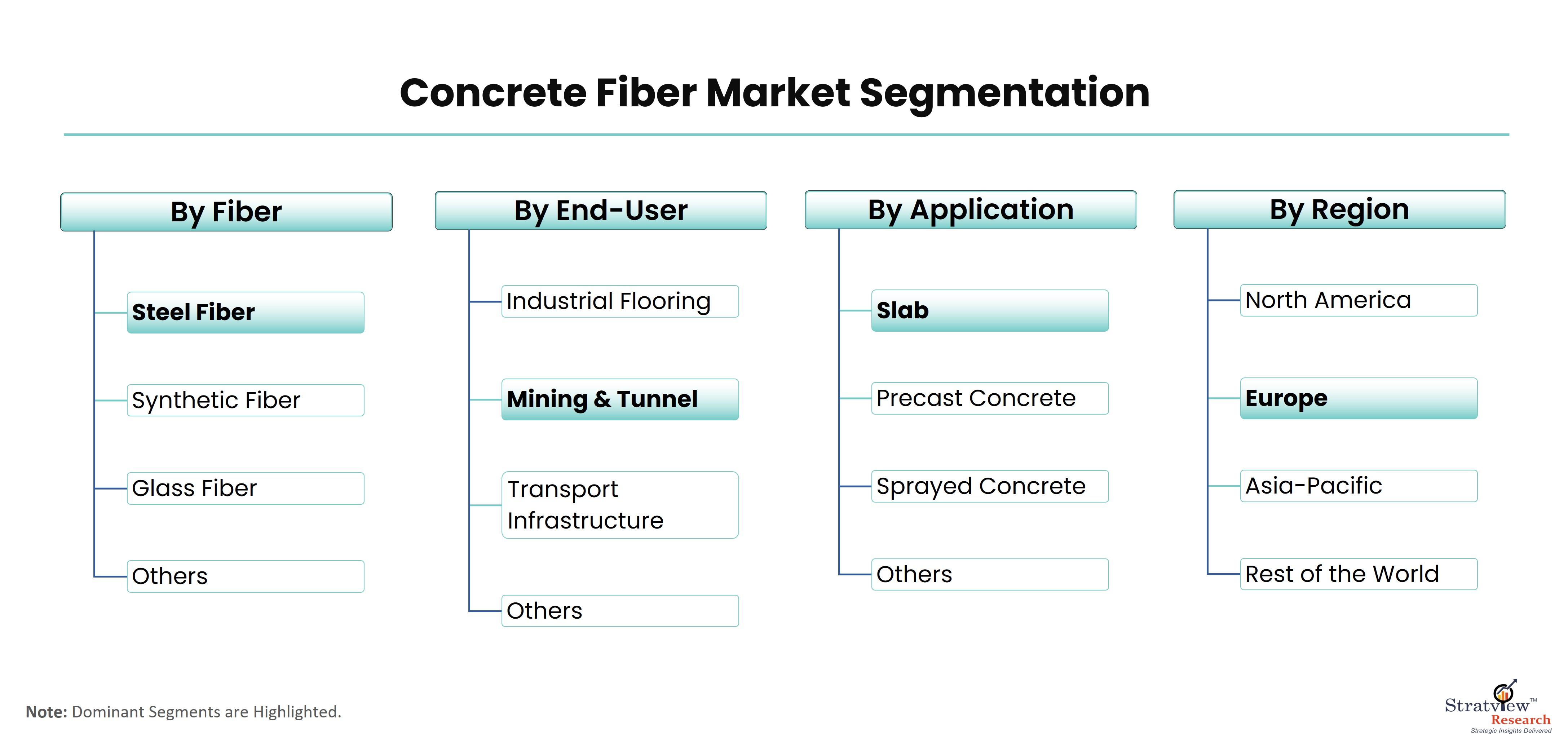
Concrete fibers are reinforcements added to the concrete mix to improve its performance, durability, and flexibility. These fibers come in various materials, each contributing unique properties to the final concrete composite. The primary types include:
Steel Fibers: Known for their high tensile strength, steel fibers are commonly used to reinforce concrete. They enhance the toughness of concrete, making it more resistant to cracking and improving its performance under heavy loads.
Polypropylene Fibers: These synthetic fibers are lightweight and resistant to chemicals. Polypropylene fibers are effective in reducing plastic shrinkage cracks and improving the impact resistance of concrete. They are often used in applications where corrosion resistance is essential.
Glass Fibers: Glass fibers offer excellent corrosion resistance and are particularly suitable for applications where electrical conductivity is a concern. They are also known for their compatibility with decorative concrete surfaces.
Basalt Fibers: Derived from natural basalt rock, these fibers provide a combination of high strength and durability. Basalt fibers are valued for their fire resistance and are an environmentally friendly alternative to some synthetic fibers.
Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of concrete fibers makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Construction and Infrastructure: Concrete fibers play a crucial role in the construction of buildings, bridges, and highways. They enhance the structural performance of concrete, offering solutions for both precast and cast-in-place applications.
Transportation: In the transportation sector, concrete fibers are used to improve the durability of pavements and reduce the occurrence of cracking. This extends the lifespan of transportation infrastructure and lowers maintenance costs.
Mining and Tunneling: Harsh environmental conditions in mining and tunneling projects demand robust construction materials. Concrete fibers provide the necessary reinforcement to withstand the challenges posed by underground environments.
Industrial Flooring: In industrial settings, where floors are subjected to heavy traffic and potential chemical exposure, concrete fibers enhance the durability and abrasion resistance of flooring systems.
Quality Control and Testing:
Ensuring the effectiveness of concrete fibers involves rigorous quality control and testing procedures. Manufacturers and construction professionals alike must adhere to industry standards to guarantee the desired performance characteristics of fiber-reinforced concrete.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of modern construction, the Concrete Fiber Industry stands as a beacon of strength and innovation. The comprehensive guide above serves as a roadmap, providing insights into the diverse world of concrete fibers, their applications, and the critical role they play in fortifying our structures. With strength in every strand, the Concrete Fiber Industry continues to shape the landscape of construction, offering solutions that endure and fortify the foundations of our built environment.